Universal risk management
The new ISO 9001:2015 standard is intended to promote the sustainable market positioning of companies. In addition to the risk-based approach, however, opportunities should also be perceived and implemented.
Synprovis GmbH has created a universal module "Risk Management " within the QM software. This enables ISO-certified SMEs to efficiently manage the requirements of the revised ISO 9001:2015 standard. The basic approach "improve" integrates risk management into the overall context of optimized quality management and a continuous improvement process (CIP). The flexibility and simplicity of the Improve web software are also reflected in the new module, which covers all types of risk (strategic, operational, technical, financial) and creates transparency from recording to monitoring.
Facts and benefits
All processes are on one platform: The module makes selective Excel solutions just as superfluous as (departmental) specialized software: Only one system to be maintained instead of individual solutions running in parallel.
Integrated into overall QM: Risk Management can be linked to all 16 existing Improve input screens and modules.
Simplicity in four steps:
1) Identify and analyze risk,
2) evaluate and classify,
3) Define measures,
4) monitor.
Defined assignment of persons: Control of measures and monitoring are assigned to persons, which creates explicit responsibilities and eliminates the risk of "shipping".
Simplicity in the 4 rhythm
The consistent structure "record, decide, do, improve" makes the KVP software user-friendly across all topics, from recording to effectiveness control. This fourfold structure is a common thread throughout Improve and can also be found in the new "Risk Management" module (see figure):
1. identification & analysis
The responsible notifier assigns an event or a potentiality to a (company-specific formulated) risk category and a risk area. He describes the risk and notes possible causes.
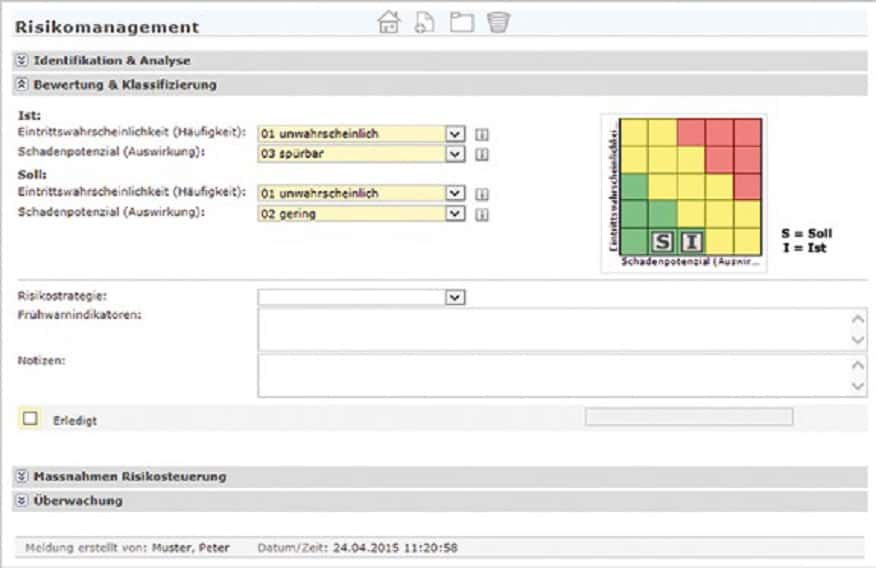
2. evaluation & classification
The risk is assessed according to the classic "probability of occurrence/loss potential" matrix for an actual and a target value. In addition, the risk strategy is defined here and suitable early warning indicators are named.
3. measures Risk management
Assignment of measures to persons and deadlines. This may sound banal, but in reality it is crucial for success. Without explicit responsibilities, no one is accountable, "risk of shipping"!
4. surveillance
Is again assigned to a person who reassesses the original assessment including the measures in the sense of the closed-loop approach.
It should be noted that the four steps do not follow a rigid chronology. In particular, steps 3 and 4, measures and monitoring, run in parallel.
Conclusion:
Well structured and usable for all corporate risks, the software integrates risk management into the overall context of quality management and CIP. The tool requires clear responsibilities for risks and their elimination and avoids any loss of information. The self-explanatory web software also impresses with its unique simplicity at the front end and thus also with short introduction and training times.









