How blockchain technology and business work
Blockchain technology is suitable for a wide range of applications. The author looks at the possibilities from the perspective of identity and access management (IAM).
Blockchain technology first became known in connection with the cryptographic currency Bitcoin. When one speaks of security, the mechanisms and the relevant guarantees behind it, one usually means the type of blockchain used by Bitcoin. The blockchain network consists of a number of independent participants that communicate with each other via broadcasts. The main design features of blockchain technology are the absence of central instances, a consensus mechanism and the immutability of the blockchain.
Blockchain and security: how does it work?
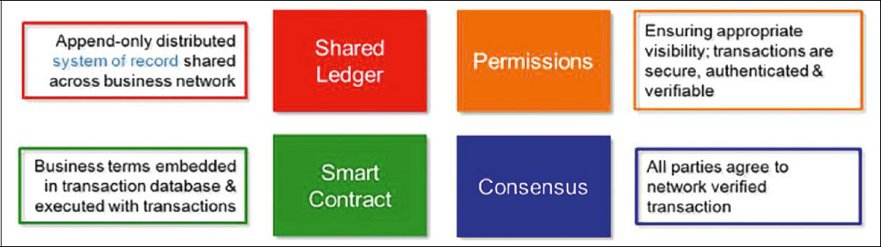
Blockchain is designed to transform transactions with the potential that the Internet did with information. Blockchain is a technology that increases trust and efficiency in the process of exchange between different parties. In this context, there is often talk of "middlemen" becoming superfluous. This can affect large parts of the business models of industries such as insurance and banking, such as Bitcoin, but also many other areas, such as the processing of a house purchase. Everything that has a value can be tracked and traded efficiently and trustworthily via a blockchain. An important element of this is the "shared ledger". This transparent ledger contains all transactions (blocks), encrypted and in chronological order (chain). By means of references (hash) to the last transaction, it is ensured that there are no unauthorized changes. This means that access is read-only. The only exception is the creation of a new block. A new transaction is validated by a consensus mechanism in the network. Further elements are so-called smart contracts, with which conditions are incorporated into the processing of the transactions, whereby these can run automatically. Permissions are used to define who has access to which attributes of which transactions.
Blockchain, security and the importance for identity and access management
Thus, the blockchain network makes economic sense as it eliminates multiple efforts and reduces intermediaries, and blockchain technology reduces market frictions in the areas of information, transaction and innovation, leading to more efficient markets. With the concept of permissions, it is most obvious that Blockchain also involves the issue of access. A blockchain network also has to deal with the usual issues around identities and access, because in the sub-area of the non-public, so-called "permissi-oned" blockchain, identification and access control basically play the same role as in classical transactions.
Fields of application, benefits and limitations
Blockchain technology also increases trust and efficiency within an organization or a network in the area of identity and access. We consider the following areas to be useful areas of application:
- Identity Provider (IdP)Providers of identities within companies can increase trust and reduce security against data theft through a decentralized structure. The IdP thus increases its level of assurance (LoA). With the inclusion of biometric data, even the highest requirements can be met.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Central Authorities (CAs): Blockchain has by far the greatest transformational power in the area of public key infrastructures and central authorities (here in terms of identities and certificates), replacing them with decentralized trust mechanisms and decentralized (infra-)structure.
- Federation: The area of federation is predestined for blockchain, since "trust" is central within the federation. Today, various IdPs are integrated for this purpose. With blockchain technology, one or more common but decentralized IdPs can be implemented. The entire federation thus benefits from higher security and transparency.
Integrating blockchain solutions into the IAx landscape
It can be very interesting and efficient for companies to integrate existing blockchain solutions into their IAx landscape or to implement them together with an IAM solution in order to outsource processes such as "Know-your-Customer (KYC)" and thereby reduce costs. Here are some examples of such existing solutions:
- Shocard: A blockchain-based identi- ty card (https://shocard.com/)
- Blockstack: "The New Internet" for decentralized apps gives developers the tools to implement identity, storage and to- kens (https://blockstack.org/)
- OneNameA registrar (cf. domain name registrar) for identities (https://onename. com/).
But: no system can be considered 100 percent secure. The blockchain offers a high level of data security thanks to its underlying functions. And yet: Organizations should not rely on it alone and should analyze their overall concepts for information and data security in depth with their trusted specialist and be concerned about adapting security on an ongoing basis.









