Digitization of industry: inequalities can jeopardize sustainable development
When individual countries or even certain sectors are left behind in digital development, this is a cause for concern. A new study provides insights into the extent of inequalities in the use of digital technologies.
With UN Sustainable Development Goal 9, the international community aims to promote sustainable industry and infrastructure. The digitization of industry can influence market access and the positioning of companies in sustainable value chains. "Environmental management along the supply chain can be improved through the use of digital technologies. This is because they can continuously provide data and thus improve transparency. This makes sustainability risks such as relocation to countries with lower social and environmental standards visible and gives us clues as to how global value chains can be made more sustainable," explains Silke Niehoff from the Institute for Transformative Sustainability Research IASS in Potsdam. She adds that However, investment in digital tools and the necessary skills would still be lacking in some countries.
Digitization of industry: Smaller companies have some catching up to do
Silke Niehoff is co-author of a comparative study entitled. "Sustainability related impacts of digitalisation on cooperation in global value chains". The study examines digital development in the emerging markets of China and Brazil and the industrialized country of Germany. Employees in companies of various sizes and in several sectors were surveyed.
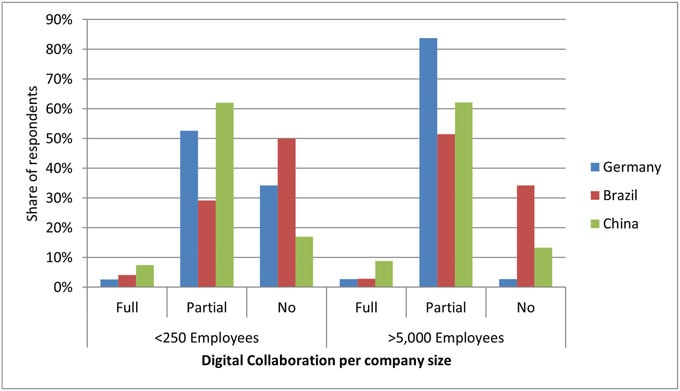
The researchers were able to show that the inequalities at country level are not as pronounced as experts had predicted. However, clear differences emerged within all countries, between different sectors and companies of different sizes. In all countries, fewer than 10 percent of companies said they would fully digitize their processes for working with partners. Partial digitization, on the other hand, is more widespread: 46 percent of Brazilian, 61 percent of Chinese and 63 percent of German companies currently already work in this way.
Large companies are making greater use of the opportunities offered by digitization than small and medium-sized enterprises in all three countries. "However, SMEs form the backbone of national economies and should not be left behind. Therefore, global governance is needed to capture inequalities at the country level, and additionally national support policies to strengthen SMEs," says co-author Grischa Beier from the IASS.
Automotive sector is a digitalization pioneer
Opportunities for more sustainable production could be provided by fully digital integration of production data into companies' environmental management systems. It potentially simplifies environmental compliance and the environmental certification process for companies and regulators, which often require analysis of the entire value chain. However, only 9 percent of German companies, 3 percent of Brazilian companies and 6 percent of Chinese companies currently use this option.
In Germany, 84 percent of respondents from the automotive sector reported at least partial digitization of collaboration processes, compared with 72 percent of Chinese and 62 percent of Brazilian companies. More than in other sectors, the number of cooperation partners among the companies surveyed has decreased as a result of the digitization of processes, while the quality of cooperation has improved as a result, according to the respondents. According to the authors, the automotive sector is an interesting object for future research: other companies could benefit from an evaluation of the experiences from this sector on their way to more sustainability.
Source: IASS









