Fraunhofer Institute publishes process model for AI engineering
Projects in which artificial intelligence (AI) is to be implemented are usually complex, require heterogeneous teams and carry a high risk of failure. How does a company manage to lead AI projects to success even in demanding application domains such as mobility or industrial production? Researchers at the Karlsruhe Competence Center for AI Engineering have developed a systematic process model.

The challenges in AI engineering arise from the characteristics of AI-based methods: The performance of technical systems that use machine learning (ML) methods can often only be poorly estimated in advance. This makes it difficult to make reliable statements about safety and reliability. This is offset by a large potential benefit: Successfully used, data-driven methods can often make decisions faster and better than would be possible with classically developed methods. In this way, they support humans, relieve them and complement them. In industrial production, ML processes lead to higher-quality and thus longer-lasting products, increase resource efficiency or enable predictive maintenance. In the field of mobility, ML processes can increase driving safety, e.g. by emergency braking in dangerous situations, and thus save lives.
In order to integrate AI-based components effectively and efficiently into existing or new applications, a systematic approach is essential. Established systems engineering process models are intended for complex technical systems. However, the use of AI and ML brings new challenges that a dedicated process model should explicitly address.
Systematically develop and operate AI solutions with AI engineering
PAISE® (a registered word mark for Nice Class 9 and 42 products), the Process Model for AI Systems Engineering, is specifically designed for the development and operation of AI-based systems. It combines approaches from computer science and data-driven modeling with those of classical engineering disciplines to overcome challenges. AI Systems Engineering, translated as AI Engineering, is what the scientists* call the interdisciplinary approach they have been working on since mid-2020. "With AI engineering, we want to systematize the development and operation of AI-based solutions. Only if AI methods can be used reliably from an engineering perspective will there be an opportunity to leverage the high value creation potential," says Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Jürgen Beyerer, head of Fraunhofer IOSB and the scientific directorate in CC-KING, the Karlsruhe Competence Center for AI Engineering. "With PAISE®, we have created a set of tools that also provides small and medium-sized enterprises in particular with a practical guide to achieve this goal."
During development, it can be difficult to estimate the performance of an overall cyber-physical system with AI components in advance. "This means that changes to the high-level design of the overall system may still be necessary at a late stage," says Constanze Hasterok, a scientist at Fraunhofer IOSB and editor of the PAISE® model. "Among other things, this effect occurs when the final ML models are trained with data from real operations. For new developments, however, high-quality data from operation is typically only available at a late stage." For operations, he says, monitoring and ideally automatic adjustment of ML models is necessary when systems and their environmental conditions can change over time.
In addition, there are personnel difficulties: As a rule, companies - especially medium-sized ones - do not have their own AI experts. At the same time, managers need to know which AI expertise should be available in the long term for the operation of AI-based systems and how the development process and its interim results are to be evaluated.
Customizable development through checkpoints
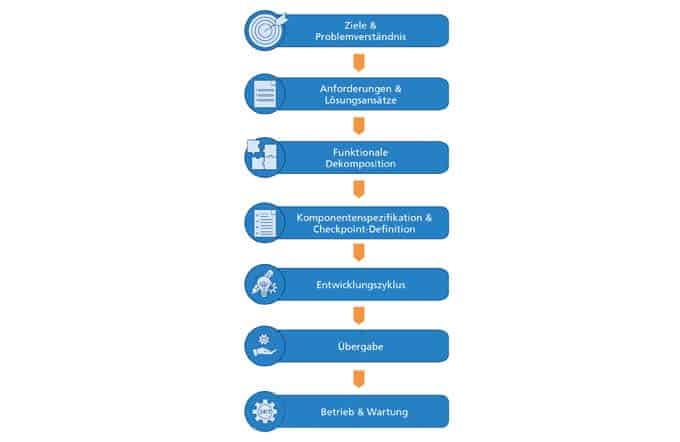
PAISE® divides the development process into seven phases. Project teams in companies must first create a common understanding of the problem, define goals and requirements, and collect solution approaches. The product is then divided into subsystems based on the requirements. This so-called functional decomposition is not final; this is where the model's agile approach begins. The development of the individual components proceeds cyclically, step by step the subsystems are refined and checked for compatibility. Each run increases the maturity of the overall system.
Checkpoints play an important role in this, as Hasterok explains: "The checkpoint-based concept of PAISE® enables a flexible development process. ML methods often require an explorative approach: You develop an ML component on a test basis and empirically check whether it is suitable for the desired purpose. Other subsystems require a targeted approach, for example according to established systems engineering methods for electronic components. In PAISE®, the individual systems are developed in parallel, each according to a domain-specific appropriate procedure." The checkpoints synchronize the development status of the subsystems early in the project and evaluate their interaction as an overall system. "In contrast to classic milestones, the targets are not firmly defined for all checkpoints at the beginning of the project," she continues. "If, for example, it turns out that an ML-based method is not the right tool after all, statistical methods can be used, the suitability of which is evaluated in the following checkpoint."
Four continuous artefacts create framework conditions
The organization of heterogeneous teams also benefits from this: Participants with different competencies meet regularly and can discuss cross-sectional aspects such as safety, cost or ethical issues. The role distribution of PAISE® defines phase-specific functions and responsibilities.
In addition to the distribution of roles, there are three other continuous result documentations (artifacts) in PAISE®: The system model describes dependencies of the individual components; the documentation for external audits includes aspects that are required for an audit by third parties such as authorities; and the data documentation records metadata of the data used, such as its source, quality, pre-processing steps and framework conditions of the data extraction.
"By providing systematic methods, we want to encourage companies and developers to tackle AI projects. PAISE® is a big step forward in this respect. It maps the entire process from conception and data acquisition to operation and maintenance, and addresses all the difficulties that can arise from a technical perspective during the implementation of an AI project," explains Dr.-Ing. Thomas Usländer, head of department at Fraunhofer IOSB and project manager of CC-KING.
A white paper on this topic is available available for download here.