Age of AI: regions need to work together more
As part of the 77th Locarno Film Festival, digitalswitzerland organized an event on the topic of artificial intelligence with a focus on Switzerland, technology in art and the power of collaboration between regions.
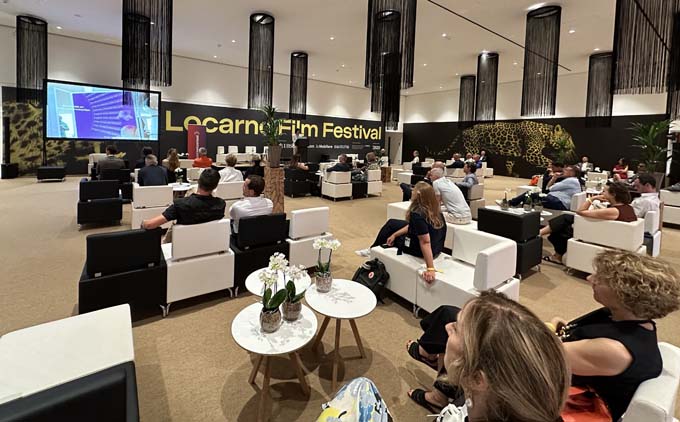

The digitalswitzerland organization has made it its mission to unite the private sector, the public sector, the academic community and the population of all language regions in Switzerland around a digital agenda. Such an agenda should lead to Switzerland becoming a leading nation in terms of innovation, business location and digital competitiveness. With this in mind, digitalswitzerland invited experts, visionaries, industry pioneers and innovative companies from the public and private sectors as well as academia to the PalaCinema Locarno on August 7 to highlight the revolutionary impact of artificial intelligence on the modern business world. The event focused on three forward-looking questions: How can the Swiss creative tech ecosystem develop? How can Switzerland benefit from the supercomputers in Ticino? Why do the regions need to join forces in the age of AI?
The future of film and the audiovisual arts
Raphaël Brunschwig, Managing Director of the Locarno Film Festival, Andreas Meyer, President of digitalswitzerland, and Stefan Metzger, CEO of digitalswitzerland, opened the event. Stefano Rizzi, Head of the Economic Affairs Department of the Canton of Ticino, and Mauro Silacci, Head of the Finance and Economy Department of the City of Locarno, followed with some introductory words.
Art had a special place in connection with the Locarno Film Festival. Kevin B. Lee, Professor of the Future of Cinema and Audiovisual Arts at the Università della Svizzera italiana (USI), raised questions about the influence of artificial intelligence on art, artists and cinema in particular: How will the importance of cinema develop in the coming years? How does cinema envision its own survival? How are artists using this new technology - and how do audiences classify AI-generated art? His conclusion, inspired by Microsoft's closing words at the 2024 Cannes International Film Festival: Artificial intelligence is not creative - you are. But the "you" defines the value, the degree of acceptance and the reasonable disruption that AI brings with it.
AI and its many facets: from creative tech to the Swiss supercomputer
Marco Zaffalon, Professor at the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence (IDSIA, USI-SUPSI), began by explaining the history of artificial intelligence and its current capabilities and incapabilities. He also addressed the associated problems. He emphasized the importance of collaboration between universities, institutes, politics and industry to develop technologies and capabilities in Switzerland.
Christoph Weckerle from the Zurich Centre for Creative Economies shed light on changes in the use of AI in the cultural sector. According to Weckerle, AI was used to disseminate cultural content - today it is used to produce it. This is leading to changes that are revolutionizing the industry. Switzerland is still underdeveloped in the creative tech sector, with Weckerle pointing to a lack of collaboration at all levels. He also emphasized the importance of developing a Swiss strategic agenda for this area. There is therefore still a lot of room for progress. Giulia Lumina, ESG and Sustainability Manager at Andersen Tax and Consulting AG, explained how AI is helping them to achieve their goals.
Maria Grazia Giuffreda, Vice Director of the Swiss Center for Scientific Computing (CSCS), and Michele de Lorenzi, Deputy Director, gave an exclusive insight into the possibilities of the new Ticino center and its supercomputer "Alps", which opens its doors on September 14. The supercomputer will act as a catalyst for technological progress in the fields of artificial intelligence, machine learning and trustworthy infrastructure. Both emphasized the central role of the supercomputer as an element of trust, innovation and collaboration in Switzerland.
Joining forces
The event ended with a panel discussion on how important it is for Swiss regions to join forces in the age of AI and what obstacles need to be overcome. Milena Folletti, Digital Transformation Officer of the Canton of Ticino, Sophie Hundertmark, Consultant for GenAI and Bots, and Marco Zaffalon exchanged views on this topic. The discussion revealed that increased cooperation pools resources, drives innovation and strengthens confidence and Switzerland's global competitiveness. However, obstacles such as regional autonomy, a lack of public-private partnerships and differing legislation are slowing down progress.
The President of the State Council of the Canton of Ticino, Christian Vitta, concluded the discussion with the following topics: the progress that artificial intelligence has made possible in all sectors, the role that Ticino has played in technological innovation and the need for large-scale interregional cooperation.
Source: digitalswitzerland